| 7.7.25 defclass | Macro |
- Syntax:
-
defclass
class-name ({superclass-name}*)
({slot-specifier}*)
[[
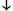 class-option]]
class-option]]
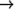 new-class
new-class
slot-specifier::= slot name| (slot-name [[ 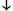 slot-option]])
slot-option]])slot-name::= symbol slot-option::= {:reader reader-function-name}* | {:writer writer-function-name}* | {:accessor reader-function-name}* | {:allocation allocation-type} | {:initarg initarg-name}* | {:initform form} | {:type type-specifier} | {:documentation string} function-name::= {symbol | (setf symbol)} class-option::= (:default-initargs ·initarg-list) | (:documentation string) | (:metaclass class-name) - Arguments and Values:
-
Class-name - a non-nil symbol.
Superclass-name--a non-nil symbol.
Slot-name--a symbol. The slot-name argument is a symbol that is syntactically valid for use as a variable name.
Reader-function-name - a non-nil symbol. :reader can be supplied more than once for a given slot.
Writer-function-name - a generic function name. :writer can be supplied more than once for a given slot.
Reader-function-name - a non-nil symbol. :accessor can be supplied more than once for a given slot.
Allocation-type - (member :instance :class). :allocation can be supplied once at most for a given slot.
Initarg-name - a symbol. :initarg can be supplied more than once for a given slot.
Form - a form. :init-form can be supplied once at most for a given slot.
Type-specifier - a type specifier. :type can be supplied once at most for a given slot.
Class-option - refers to the class as a whole or to all class slots.
Initarg-list - a list of alternating initialization argument names and default initial value forms. :default-initargs can be supplied at most once.
Class-name - a non-nil symbol. :metaclass can be supplied once at most.
new-class - the new class object.
- Description:
-
The macro defclass defines a new named class. It returns
the new class object as its result.
The syntax of defclass provides options for specifying initialization arguments for slots, for specifying default initialization values for slots, and for requesting that methods on specified generic functions be automatically generated for reading and writing the values of slots. No reader or writer functions are defined by default; their generation must be explicitly requested. However, slots can always be accessed using slot-value.
Defining a new class also causes a type of the same name to be defined. The predicate (typep object class-name) returns true if the class of the given object is the class named by class-name itself or a subclass of the class class-name. A class object can be used as a type specifier. Thus (typep object class) returns true if the class of the object is class itself or a subclass of class.
The class-name argument specifies the proper name of the new class. If a class with the same proper name already exists and that class is an instance of standard-class, and if the defclass form for the definition of the new class specifies a class of class standard-class, the existing class is redefined, and instances of it (and its subclasses) are updated to the new definition at the time that they are next accessed. For details, see Section 4.3.6 Redefining Classes.
Each superclass-name argument specifies a direct superclass of the new class. If the superclass list is empty, then the superclass defaults depending on the metaclass, with standard-object being the default for standard-class.
The new class will inherit slots and methods from each of its direct superclasses, from their direct superclasses, and so on. For a discussion of how slots and methods are inherited, see Section 4.3.4 Inheritance.
The following slot options are available:
-
The :reader slot option specifies that an unqualified method is
to be defined on the generic function named reader-function-name
to read the value of the given slot.
-
The :writer slot option specifies that an unqualified method is
to be defined on the generic function named writer-function-name
to write the value of the slot.
-
The :accessor slot option specifies that an unqualified method
is to be defined on the generic function named reader-function-name
to read the value of the given slot
and that an unqualified method is to be defined on the
generic function named (setf reader-function-name) to be
used with setf to modify the value of the slot.
-
The :allocation slot option is used to specify where storage is
to be allocated for the given slot. Storage for a
slot can be located
in each instance or in the class object itself.
The value of the allocation-type argument can be
either the keyword :instance
or the keyword :class. If the :allocation
slot option is not specified, the effect is the same as specifying
:allocation :instance.
- --
If allocation-type is :instance, a local slot of
the name slot-name is allocated in each instance of the
class.
- -- If allocation-type is :class, a shared slot of the given name is allocated in the class object created by this defclass form. The value of the slot is shared by all instances of the class. If a class C1 defines such a shared slot, any subclass C2 of C1 will share this single slot unless the defclass form for C2 specifies a slot of the same name or there is a superclass of C2 that precedes C1 in the class precedence list of C2 and that defines a slot of the same name.
- --
If allocation-type is :instance, a local slot of
the name slot-name is allocated in each instance of the
class.
- The :initform slot option is used to provide a default
initial value form to be used in the initialization of the slot. This
form is evaluated every time it is used to initialize the
slot. The
lexical environment in which this form is evaluated is the lexical
environment in which the defclass form was evaluated.
Note that the lexical environment refers both to variables and to
functions. For local slots, the dynamic environment is the dynamic
environment in which make-instance is called; for shared
slots, the dynamic environment is the dynamic environment in which the
defclass form was evaluated.
See Section 7.1 Object Creation and Initialization.
No implementation is permitted to extend the syntax of defclass to allow (slot-name form) as an abbreviation for (slot-name :initform form).
-
The :initarg slot option declares an initialization
argument named initarg-name and specifies that this
initialization argument initializes the given slot. If the
initialization argument has a value in the call to
initialize-instance, the value will be stored into the given slot,
and the slot's :initform slot option, if any, is not
evaluated. If none of the initialization arguments specified for a
given slot has a value, the slot is initialized according to the
:initform slot option, if specified.
-
The :type slot option specifies that the contents of the
slot will always be of the specified data type. It effectively
declares the result type of the reader generic function when applied
to an object of this class. The consequences of attempting to store in a
slot a value that does not satisfy the type of the slot are undefined.
The :type slot option is further discussed in
Section 7.5.3 Inheritance of Slots and Slot Options.
- The :documentation slot option provides a documentation string for the slot. :documentation can be supplied once at most for a given slot.
Each class option is an option that refers to the class as a whole. The following class options are available:
-
The :default-initargs class option is followed by a list of
alternating initialization argument names and default initial value
forms. If any of these initialization arguments does not appear in
the initialization argument list supplied to make-instance, the
corresponding default initial value form is evaluated, and the
initialization argument name and the form's value are added to the end
of the initialization argument list before the instance is created;
see Section 7.1 Object Creation and Initialization.
The default initial value form is evaluated each time it is used. The lexical
environment in which this form is evaluated is the lexical environment
in which the defclass form was evaluated. The dynamic
environment is the dynamic environment in which make-instance
was called. If an initialization argument name appears more than once
in a :default-initargs class option, an error is signaled.
-
The :documentation class option causes a documentation string
to be attached with the class object,
and attached with kind type to the class-name.
:documentation can be supplied once at most.
- The :metaclass class option is used to specify that instances of the class being defined are to have a different metaclass than the default provided by the system (the class standard-class).
Note the following rules of defclass for standard classes:
-
It is not required that the superclasses of a class be defined before
the defclass form for that class is evaluated.
-
All the superclasses of a class must be defined before
an instance of the class can be made.
- A class must be defined before it can be used as a parameter specializer in a defmethod form.
The object system can be extended to cover situations where these rules are not obeyed.
Some slot options are inherited by a class from its superclasses, and some can be shadowed or altered by providing a local slot description. No class options except :default-initargs are inherited. For a detailed description of how slots and slot options are inherited, see Section 7.5.3 Inheritance of Slots and Slot Options.
The options to defclass can be extended. It is required that all implementations signal an error if they observe a class option or a slot option that is not implemented locally.
It is valid to specify more than one reader, writer, accessor, or initialization argument for a slot. No other slot option can appear more than once in a single slot description, or an error is signaled.
If no reader, writer, or accessor is specified for a slot, the slot can only be accessed by the function slot-value.
If a defclass form appears as a top level form, the compiler must make the class name be recognized as a valid type name in subsequent declarations (as for deftype) and be recognized as a valid class name for defmethod parameter specializers and for use as the :metaclass option of a subsequent defclass. The compiler must make the class definition available to be returned by find-class when its environment argument is a value received as the environment parameter of a macro.
-
The :reader slot option specifies that an unqualified method is
to be defined on the generic function named reader-function-name
to read the value of the given slot.
- Exceptional Situations:
-
If there are any duplicate slot names,
an error of type program-error is signaled.
If an initialization argument name appears more than once in :default-initargs class option, an error of type program-error is signaled.
If any of the following slot options appears more than once in a single slot description, an error of type program-error is signaled: :allocation, :initform, :type, :documentation.
It is required that all implementations signal an error of type program-error if they observe a class option or a slot option that is not implemented locally.
- See Also:
-
documentation,
initialize-instance,
make-instance,
slot-value,
Section 4.3 Classes,
Section 4.3.4 Inheritance,
Section 4.3.6 Redefining Classes,
Section 4.3.5 Determining the Class Precedence List,
Section 7.1 Object Creation and Initialization
- Allegro CL Implementation Details:
- None.